Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
250x250
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Tags
- GPT
- Ai
- AI 경진대회
- 현대자동차
- 데이터 구축
- word2vec
- 기아
- RNN
- Bert
- passage retrieval
- Bart
- ODQA
- N2N
- Optimization
- AI Math
- seaborn
- Attention
- dataset
- N21
- 2023 현대차·기아 CTO AI 경진대회
- nlp
- Data Viz
- mrc
- 딥러닝
- Transformer
- KLUE
- Self-attention
- 데이터 시각화
- pyTorch
- matplotlib
Archives
- Today
- Total
쉬엄쉬엄블로그
AutoGrad와 Optimizer 본문
728x90
이 색깔은 주석이라 무시하셔도 됩니다.
torch.nn.Module
- 딥러닝을 구성하는 Layer의 base class
- Input, Output, Forward, Backward 정의
- 학습의 대상이 되는 parameter(tensor) 정의
torch.nn.Parameter
- Tensor 객체의 상속 객체
- nn.Module 내에 attribute가 될 때는 required_grad=True로 지정되어 학습 대상이 되는 Tensor
- default로 AutoGrad 대상이 됨
- 직접 지정할 일은 잘 없음
- 대부분의 layer에는 weights 값들이 지정되어 있음
class MyLiner(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, bias=True):
super().__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.weights = Tensor(
torch.randn(in_features, out_features))
self.bias = Tensor(torch.randn(out_features))
def forward(self, x : Tensor):
return x @ self.weights + self.biasBackward
- Layer에 있는 Parameter들의 미분을 수행
- Forward의 결과값 (model의 output=예측치)과 실제값 간의 차이(loss)에 대해 미분을 수행
- 해당 값으로 Parameter 업데이트
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Converting inputs and labels to Variable
if torch.cuda.is_available():
inputs = Variable(torch.from_numpy(x_train).cuda())
labels = Variable(torch.from_numpy(y_train).cuda())
else:
inputs = Variable(torch.from_numpy(x_train))
labels = Variable(torch.from_numpy(y_train))
# Clear gradient buffers because we don't want any gradient from previous epoch to carry forward, dont want to cummulate gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# get output from the model, given the inputs
# (모델에 입력 값을 주고 예측 값을 반환)
outputs = model(inputs)
# get loss for the predicted output
# (모델의 예측 값에 대해 loss 계산)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
print(loss)
# get gradients w.r.t to parameters
# (파라미터의 gradients 계산)
loss.backward()
# update parameters
# (파라미터 업데이트)
optimizer.step()
print('epoch {}, loss {}'.format(epoch, loss.item()))optimizer.zero_gard()- 이전 gradient 값이 현재(지금 순서) 학습에 영향을 주지 않도록 하기 위해 초기화하는 코드
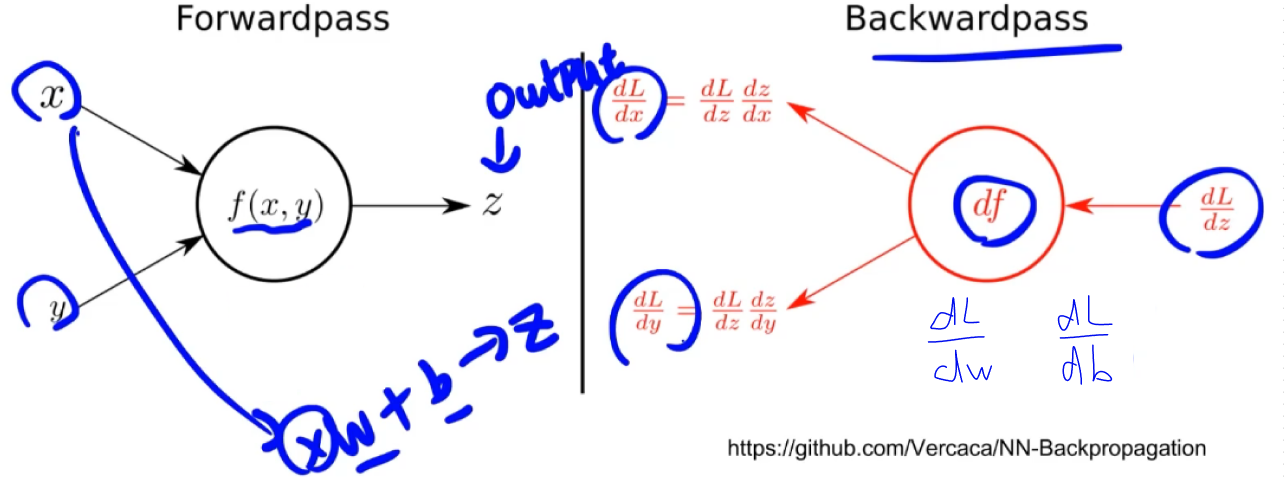
Backward from the scratch
- 실제 backward는 Module 단계에서 직접 지정 가능
- 하지만 AutoGrad가 알아서 해주기 때문에 직접 해줄 필요없음
- Module에서 backward와 optimizer 오버라이딩
- 사용자가 직접 미분 수식을 써야하는 부담
- 쓸일은 없으나 순서는 이해할 필요가 있음
class LR(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, lr=torch.scalar_tensor(0.01)):
super(LR, self).__init__()
# intialize parameters
self.w = torch.zeros(dim, 1, dtype=torch.float).to(device)
self.b = torch.scalar_tensor(0).to(device)
self.grads = {"dw": torch.zeros(dim, 1, dtype=torch.float).to(device),
"db": torch.scalar_tensor(0).to(device)}
self.lr = lr.to(device)
def forward(self, x):
## compute forward
z = torch.mm(self.w.T, x) + self.b
a = self.sigmoid(z)
return a
def sigmoid(self, z):
return 1/(1 + torch.exp(-z))
def backward(self, x, yhat, y):
## compute backward
self.grads["dw"] = (1/x.shape[1]) * torch.mm(x, (yhat - y).T)
self.grads["db"] = (1/x.shape[1]) * torch.sum(yhat - y)
def optimize(self):
## optimization step
self.w = self.w - self.lr * self.grads["dw"]
self.b = self.b - self.lr * self.grads["db"]
## utility functions
def loss(yhat, y):
m = y.size()[1]
return -(1/m)* torch.sum(y*torch.log(yhat) + (1 - y)* torch.log(1-yhat))
def predict(yhat, y):
y_prediction = torch.zeros(1, y.size()[1])
for i in range(yhat.size()[1]):
if yhat[0, i] <= 0.5:
y_prediction[0, i] = 0
else:
y_prediction[0, i] = 1
return 100 - torch.mean(torch.abs(y_prediction - y)) * 100'부스트캠프 AI Tech 4기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| PyTorch 모델 불러오기 (0) | 2023.05.19 |
|---|---|
| Datasets과 Dataloaders (0) | 2023.05.18 |
| Custom Model 제작 (0) | 2023.05.13 |
| PyTorch 프로젝트 구조 이해하기 (0) | 2023.05.12 |
| PyTorch Basics (0) | 2023.05.11 |
Comments



