| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- dataset
- 2023 현대차·기아 CTO AI 경진대회
- pyTorch
- 현대자동차
- KLUE
- Ai
- Bart
- N21
- nlp
- Bert
- AI 경진대회
- ODQA
- AI Math
- 데이터 시각화
- RNN
- 딥러닝
- word2vec
- Optimization
- seaborn
- Attention
- matplotlib
- Transformer
- Self-attention
- 데이터 구축
- mrc
- N2N
- GPT
- passage retrieval
- Data Viz
- 기아
- Today
- Total
쉬엄쉬엄블로그
모델 경량화 2강 이론 - 작은 모델, 좋은 파라미터 찾기 본문
이 색깔은 주석이라 무시하셔도 됩니다.
1. Overview
1.1 Conventional DL Training Pipeline
- Data Engineering
- Data Cleansing, Preprocessing
- Feature Engineering
- Select ML Algorithm
- Select Backbone Model(ResNet, MobileNet, EfficientNet, ...)
- Set Hyperparameters
- Loss, Optimizer, Learning rate, Batchsize, ...)
- …
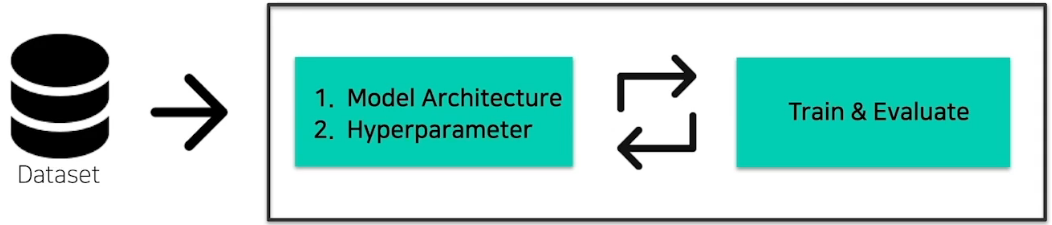
- 반복적인(Human in the Loop) Tuning 과정
- 좋은 configuration을 찾을 때까지 반복
1.2 Objectives of AutoML
- AutoML: "True" End-to-end learning

- AutoML(HPO: Hyperparameter Optimization)의 문제 정의
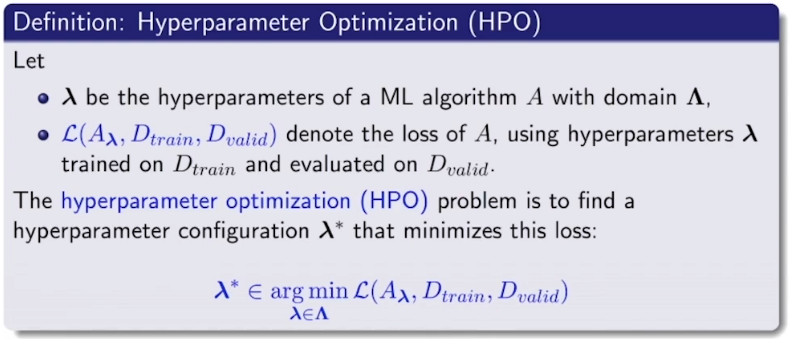
- 평가 데이터셋이 주어지고 알고리즘과 configuration이 정의되어 있을 때 loss를 최소화하는 hyperparameter configuration을 찾는 것이 AutoML의 모토
1.3 Properties of configurations in DL
DL model Configuration(Architecture, Hyperparameter)의 특징
1. 주요 타입 구분
A. Categorical
ex) optimizer: [Adam, SGD, AdamW, ...], module: [Conv, BottleNeck, InvertedResidual, ...]
B. Continuous
ex) learning rate, regularizer param, ...
C. Integer
ex) batch_size, epochs, ...
2. Conditional(★)한 configuration에 따라 search space가 달라질 수 있음
A. Optimizer의 sample(e.g. SGD, Adam 등등)에 따라서 optimizer parameter의 종류, search space도 달라짐
(e.g. optimizer에 따른 learning rate range 차이, SGD: momentum, Adam: alpha, beta1, beta2, .. 등등)
B. Module의 sample(e.g. Vanilla Conv, BottleNeck, InvertedResidual 등등)에 따라서 해당 module의 parameter의 종류,
search space도 달라짐
1.4 모델경량화 관점에서의 AutoML
(주어진)모델을 경량화하자 vs (새로운)경량 모델을 찾자
- 모델 경량화의 접근 두 가지
- 기존 가지고 있는 모델을 경량화하는 기법
- Pruning, Tensor decomposition, ...
- Search를 통하여 경량 모델을 찾는 기법
- NAS(Neural Architecture Search), AutoML(Automated Machine Learning), ...
2. Basic concept
2.1 AutoML Pipeline
일반적인 AutoML Pipeline
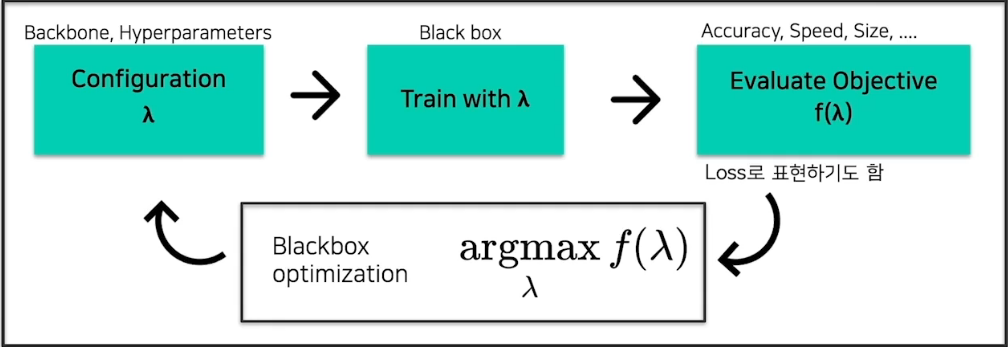
- task에 적절한 목적함수 $f(\lambda)$를 통해 $\lambda$ configuration 하는 것이 목표
AutoML Pipeline 예시: Bayesian Optimization(BO)

- Surrogate Function : $f(\lambda)$를 예측하는 regression model
- Acquisition Function : Surrogate Function을 통해 다음에 시도해 볼 $\lambda$를 결정하는 model
2.2 Bayesian Optimization(with Gaussian Process Regression)
Bayesian Optimization

- Gaussian Process Regression이 가지는 장점은 uncertainty를 모델링할 수 있다는 것
- 함수들의 분포를 정의하고, 이 분포가 Multivariate Gaussian distribution을 따른다고 가정한다.
- observation(위 그림에서 양쪽의 두 point)가 주어지고 그 사이의 값을 예측해야 하는 상황에서 실제 값이 대강 그림에서 두 점 사이의 파란 영역 내에 있을 것 같다고 예측할 수 있다.
- Surrogate Function이 $f(\lambda)$를 갱신하고 Acquisition Function이 다음 확인할 observation을 추천하는 과정을 반복하여 $\lambda$ configuration 함
Surrogate Model(Function): $f(\lambda)$의 Regression model
- Objective $f(\lambda)$ 값을 예측하는 모델
(지금까지 관측된 $f(\lambda)$들이 있을 때, 새로운 $\lambda*$에 대한 objective $f(\lambda*)$는 얼마일까?) - Objective를 estimate 하는 surrogate model을 학습, 다음 좋은 $\lambda$를 선택하는 기준으로 사용
- 대표적인 Surrogate model로는 Gaussian Process Regression(GPR) Model (Mean: 예측 f값, Var: uncertainty)

Acquisition Function:다음은 어디를 trial 하면 좋을까?
- Surrogate model의 output으로부터, 다음 시도해 보면 좋을 $\lambda$를 계산하는 함수
- Exploration vs Exploitation ("불확실한 지점 vs 알고 있는 가장 좋은 곳"의 trade off)
- 안 가본 곳에 적절한 값이 있지 않을까? 와 가장 좋았던 곳 근처에 적절한 값이 있지 않을까?
- 가장 좋았던 곳 근처이면서 안 가봤던 곳을 적절히 조합하여 다음 시도해 보면 좋을 $\lambda$를 찾음

- Acquisition function의 max 지점을 다음 iteration에서 trial
- Ex) Upper Confidence Bound(UCB)

2.2 Bayesian Optimization(with Tree-structured Parzen Estimator)
Tree-structured Parzen Estimator(TPE)
- GPR의 약점
- inverse matrix를 계산해야 하기 때문에 O(N**3)의 높은 시간복잡도를 가진다.
- Conditional(★), cont/disc 파라미터들의 혼재 시 적용이 어렵다.
- 후자의 이유 때문에 GPR보다는 TPE를 많이 사용
- TPE: GPR($p(f|\lambda)$)과 다르게 $p(\lambda|f)$와 $p(\lambda)$를 계산
TPE를 통한 다음 step의 lambda 계산 방법
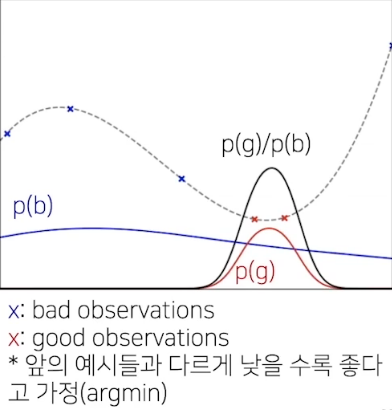
- 현재까지의 observation들을 특정 quantile(inverse CDF)로 구분
(ex: 전체 중 75% bad, 25% good) - KDE(Kernel density estimation)으로 good observations 분포(p(g)), bad observations의 분포(p(b))를 각각 추정
(greater의 분포, lower의 분포) - p(g)/p(b)은 EI(Expected Improvement, acqusition function 중 하나)에 비례하므로, p(g)/p(b)가 가장 높은 값을 가지는 $\lambda$를 다음 step으로 설정
- p(g) : good observations, p(b) : bad observations
- p(g)/p(b)가 높은 지점을 탐색한다?
- => 좋았던 관측 분포가 높은 쪽을 선호하되, 안 좋은지 알 수 없는 것도 찾아보자는 의미
- Surrogate Function을 update 하고 Acquisition Function을 계산하는 과정을 이 step으로 계산할 수 있게 됨
너무 어려워...
Tree-structured Parzen Estimator(TPE): EI 증명
- Likelihood를 Quantile로 구분되는 두 함수로 정의

3. Further Studies
3.1 한계점 및 연구 키워드
가장 큰 문제: 시간
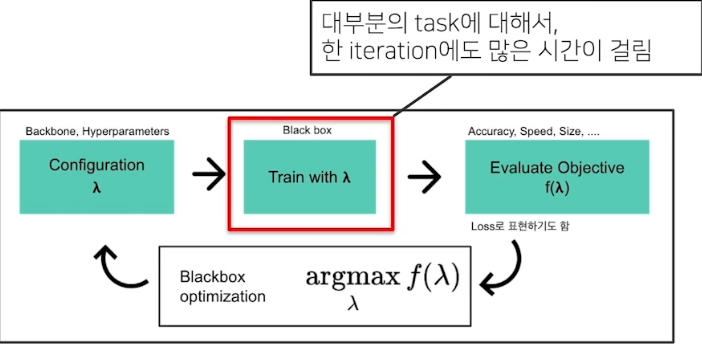
아직은 활발한 연구분야
- DL에서의 AutoML은 scalability 이슈가 더욱 대두됨
- 주요 키워드
- Hyperparameter Gradient Descent(탐색과 학습을 동시에)
- Meta-learning(Auto "AutoML")
- Multi-fidelity optimization
- Data의 subset만을 활용
- 적은 epoch
- RL을 활용한 적은 trial
- Image Downsampling 등등
3.2 현실적인 접근
절충안: 그럼에도 불구하고
- 아직 문제들이 크리티컬 하지만 충분히 절충 가능(Where engineering comes in)
- 어느 정도의 prior를 개입, 탐색 공간을 작게,
- 적지만, 대표성을 띄는 좋은 subset 데이터를 정하고(+ n-fold Cross validation 등의 테크닉)
- 학습 과정의 profile을 보고 early terminate 하는 기법 적용
(ASHA Scheduler, BOHB(Bayesian Optimization & Hyperband)
등등의 방법으로 사람의 단순 반복보다 "충분히 좋은" configuration을 찾을 수 있다.
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/2011/file/86e8f7ab32cfd12577bc2619bc635690-Paper.pdf
https://direct.mit.edu/books/book/2320/Gaussian-Processes-for-Machine-Learning
Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning
A comprehensive and self-contained introduction to Gaussian processes, which provide a principled, practical, probabilistic approach to learning in kernel machi
direct.mit.edu
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7352306
Taking the Human Out of the Loop: A Review of Bayesian Optimization
Big Data applications are typically associated with systems involving large numbers of users, massive complex software systems, and large-scale heterogeneous computing and storage architectures. The construction of such systems involves many distributed de
ieeexplore.ieee.org
https://www.boostcourse.org/ai302/joinLectures/374476
딥러닝 모델 더 작게 만들기(경량화)
부스트코스 무료 강의
www.boostcourse.org
'AI' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 모델 경량화 2강 실습 - 작은 모델, 좋은 파라미터 찾기 (0) | 2023.05.25 |
|---|---|
| ChatGPT : 새로운 자연어 처리기술의 발전과 가능성 (0) | 2023.05.22 |
| F Beta-Score? (0) | 2023.05.14 |
| ChatGPT Prompt Engineering for Developers (0) | 2023.05.08 |
| 모델 경량화 1강 (0) | 2023.05.01 |



